It can be realized immediately or secondarily. I usually use a tissue expander,
placed in sub muscular position, that will be swollen post-operatively every 3 to 4 weeks with saline solution. The expander will be changed within 4 to 12 months to a final silicone prosthesis. This techniques enables the patient to choose the volume as the expansion takes place.
The use of an expander in immediate reconstruction diminishes scar tension and the risk of complications. In secondary reconstruction, the expander enables to get a well-marked mammary fold without having to perform a skin and fat flap advancement and the risks that it involves. In my experience,the risk of failureof breast reconstruction with prosthesis using anexpanderis low (3%), compared to the riskof complicationsafter introduction of apermanent prosthesisimmediately, (5 to20%according to literature), especially for patients who smoke.
The inconvenience of having to carry out a second operation is not only compensated by a lower risk, but also by the opportunity to obtain a better final result:
-by using anatomic implants when replacing the expander, giving out a more natural curve than round prostheses
- remodeling easily the space for the prosthesis, if the height of the fold or the implant’s width needs to be modified.
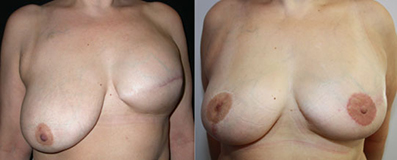
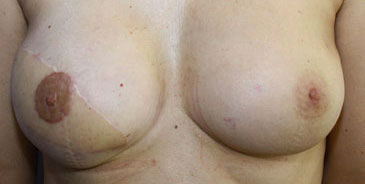
From Left to Right :
Expander infra-mammary fold too high, Lowering of the fold through prosthesis exchange and opposite breast reduction
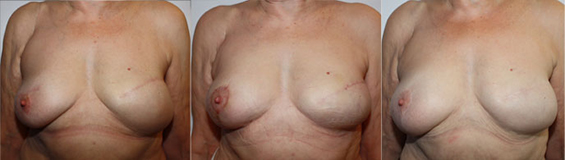
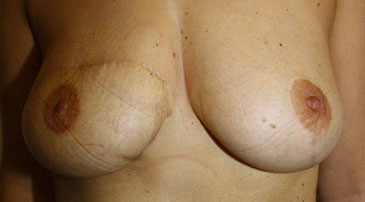
From Left to Right :
Expander Infra-mammary fold too low
After correction and symmetrization
Stable result over time
-associating it with a lipofilling to improve the aspect of the reconstruction
-allowing a more accurate symmetrization surgery of the opposite breast, as we have a better idea of the final result after reconstruction with prosthesis
It is often indicated to have an opposite breast augmentation for small or average-sized breasts, to optimize the final result.
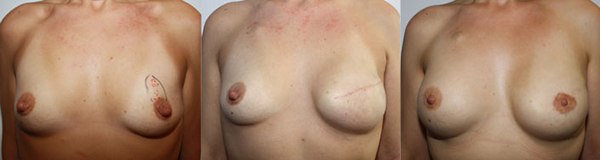
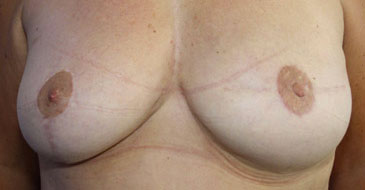
From Left to Right :
A-Cup breasts, DCIS of the left breast
Full mastectomy and expander
Final result after opposite breast augmentation
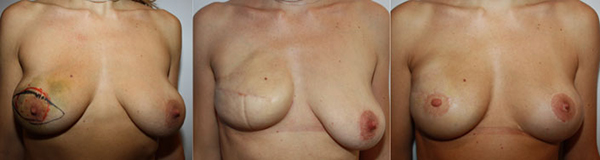
From Left to Right :
B-Cup breasts Right retro-areolar cancer
Full mastectomy and expander
Final result after opposite breast augmentation and mastopexy
Sometimes a reduction,
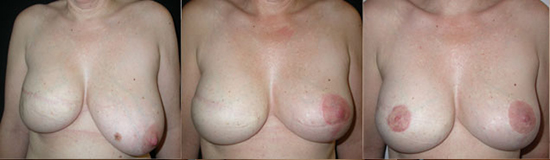
From Left to Right :
Right breast full mastectomy and expander D-cup left breast
Final result Right prosthesis exchange opposite breast reduction
Final result
or a simple symmetrization mastopexy,
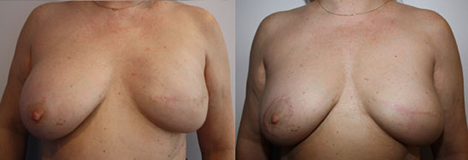
From Left to Right :
Left breast full mastectomy and expander, C-Cup right breast
Final result after left breast prosthesis exchange
and opposite breast mastopexy
is carried out on the opposite breast, but the risk of asymmetry increases over time.
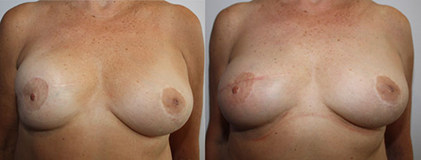
From Left to Right :
Breast asymmetry 7 years after right breast reconstruction with prosthesis
Correction using Pepriprosthetic capsule with prosthesis exchange and lipofilling
Other techniques

 English
English
 Français
Français
 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国)
 Español
Español
 Português (BR)
Português (BR)